Are they just a pair of Glasses?
 |
| Google Glass as a Pair of Glasses! |
I just read an interesting article, one of the many that has
been popping up over the past month or two relating to the new Google Glass,
the most recent and probably to date, the most advanced proposition for a real
“wearable computing” solution.
I have to
admit some confusion regarding the name, for some reason I appear to refer to
Google Glass continuously in the plural, mainly because it bears at least a
material resemblance to the existing wearable AT solution that sits on the
bridge of my nose!
Google Glass is not available as a product yet, (and of
course neither are “Google Glasses”) although it seems like people have been
talking about it for quite a while. In
fact applications for Google Glass, according to their website have closed, http://www.google.com/glass/start/how-to-get-one/. With announcements for their early adopter
program due shortly and the promise of a consumer model late in 2013.
The article by Natasha Lomas (http://techcrunch.com/2013/03/31/glass-explorer-apps/)
presents a great update on the project as a whole and presents a digest of some
of the many ideas posed by applicants to the Google Glass Explorer Program, a process running
in early 2013 for anyone who wanted to apply requiring them post their proposed
innovations on Google+ or Twitter consisting of 50 words or less, featuring the
hashtag #ifihadglass.
One can only assume that this privileged community of, rumor
has it, 1500 people will become the new pioneers in the next generation of
mobile or wearable technology solutions.
Google Glass is
a wearable computer with a head-mounted display (HMD) that is being developed by Google in the Project
Glass research and development project, see
the Wikipedia entry for further information http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Glass . I also wonder if the 007 nature of such
technology coupled with the fact that it is being developed in somewhere called
“Google X Lab” alongside a “driverless car”, has added to the hype about it?
Since talk about Google Glass has been doing the rounds for
longer than the Apple Watch, it despite all of the talk and hype, there is
nothing for the public to judge beyond sound-bites and speculation. However, as blogs are a natural home for
speculation – we will indulge ourselves here with some speculation as to what
Google Glass might mean for people with a disability or the accessibility
community.
Often we are witness to new revolutions in technology leaving
people with a disability floundering in its wake, or disenfranchised in the
enthusiasm of the latest and greatest trend.
Does anyone from the blind community remember the launch of the Graphic
User Interface – or going back further, how long it took for members of the
Deaf Community to make up for ground lost by Bell’s groundbreaking “telephone”?
In her article, Natasha Lomas compiled a list of the app
ideas that Glass winners are pledging to create, interestingly there are
several potential applications for People with a Disability or otherwise
improve the accessibility of the ICT landscape.
Some of the examples include:
- I want to make an app that helps deaf people “see” what others are talking about
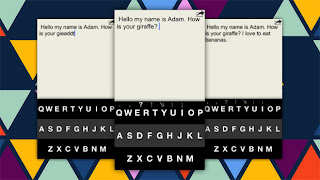
- I would develop an application to enable the communication with deaf people by showing a live transcription in Google Glass 1/2
- I would design an app to notify the deaf when a loud noise identifies a hazard outside of their field of view
- Think about applications for use with kids and learning disabilities.
It was heartening to see the list of potential apps that
might be created for people with a disability, particularly after watching the
promotional video which appears on the “How It Feels” section of the Google
Glass website http://www.google.com/glass/start/how-it-feels/
(how accessible is that?), which would suggest that this revolution in wearable
technology is nothing other than a home movie camera for families and adrenalin
junkies.
So many of the ideas posed relate to solutions for People
who are Deaf or Hearing Impaired, curious that developers obviously see
potential in a technology that clearly looks like its for people with
low vision, to be transformed into a device that helps deaf or hearing impaired
people communicate.
For those, like me, who were neither brave enough or
organized enough to submit my ideas in 50 words or less using the hashtag
#ifihadglass – I now offer the opportunity to post your speculations as to what
the “killer” APP for the Assistive Technology or Accessibility communities will
be right here.
For people with
Dyslexia: An App that highlights each word as the person moves their eyes
over text or documents and used text to speech to “read aloud” for the person.
·
For adults with low
vision: An App that magnifies text to a selected font size, and renders
this in the person’s field of vision.
This would be particularly useful for older people who struggle to read
the prices or information on labels when shopping.
·
For people with
restricted mobility: An app that allows environmental control via eye gaze
(if eye gaze technology can be scaled to such a degree). Allowing a person with limited mobility to
look at an object and change its state (on/off etc.) would be a huge step
forward from the current switch and scanning solutions currently available.
·
For Young Adults with a
Learning Disability: An APP that could act as a “travel partner”, assisting
young adults with cognitive disabilities with learning how to travel or take
transportation independently.
·
For Children with
Communication Disabilities: An APP that provides text to speech feedback
for objects a child is looking at, providing an opportunity for a parent or
therapist to gain better insight as to the child’s ability to eye-point to
objects in his/her environment. Although
the main challenge would be to stop the child from continuously taking the high
tech specs off!!!
Anyway – this is just for starters. I, for one, am not sure if the final Google
Glass that we will eventually see, will live up to expectations. It is easy however, to sit on the sidelines
and remain skeptical, instead it’s a lot more productive to :imagine”. With that thought in mind, I would love to
hear anyone else’s speculations about what Google Glass might offer people with
a disability. Tweet it, share it, blog it – it certainly makes for some interesting thinking and conversations!